Description
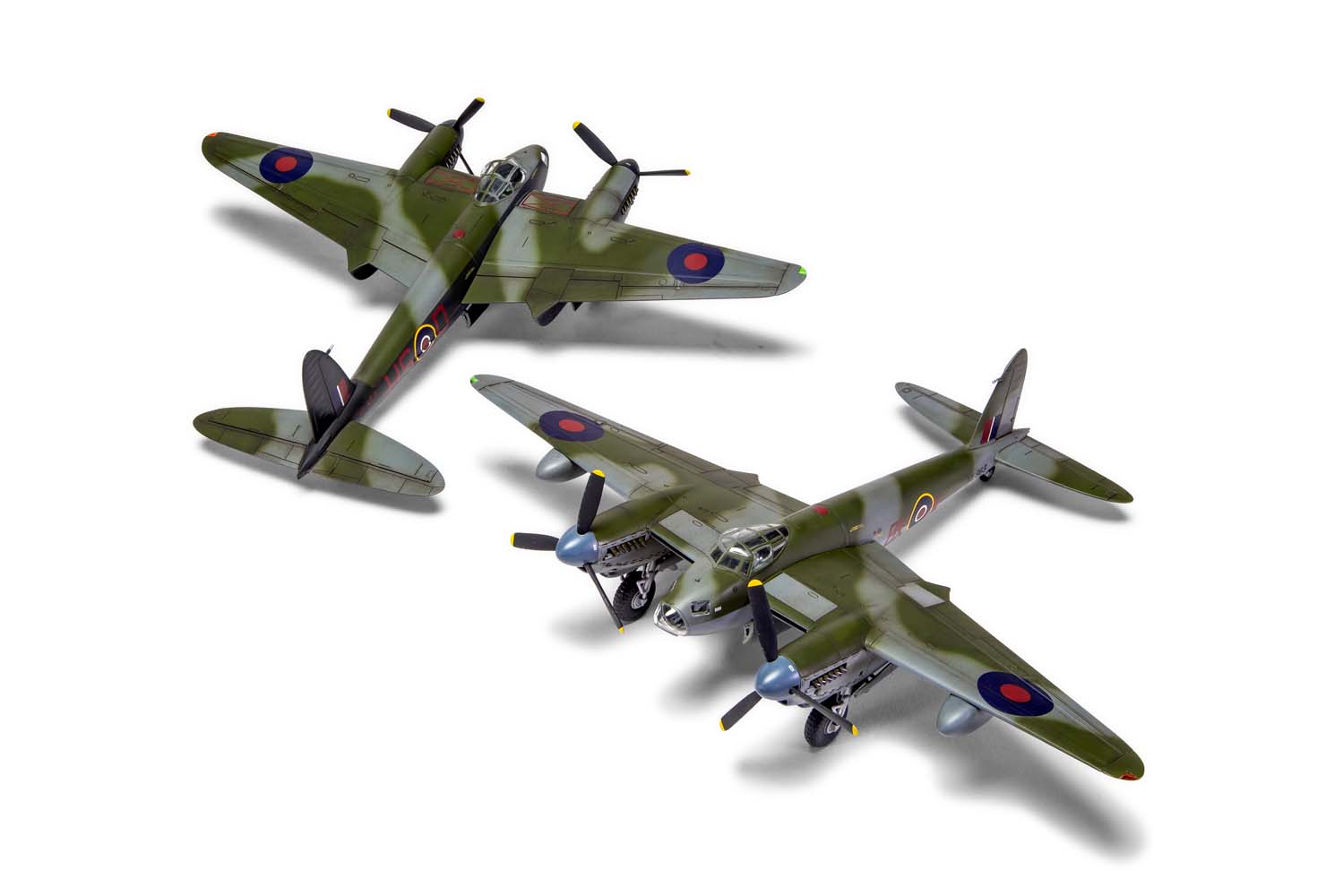
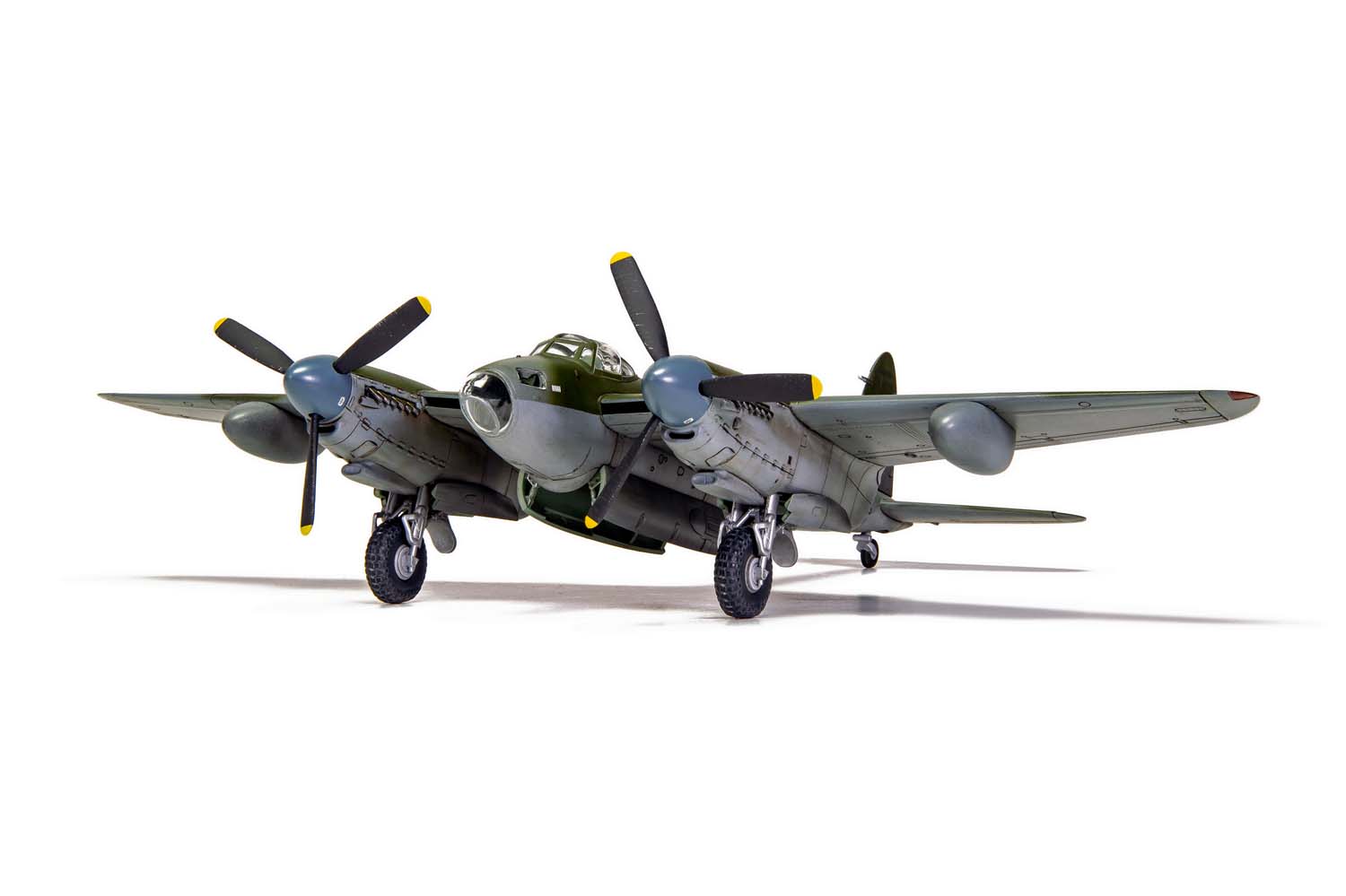
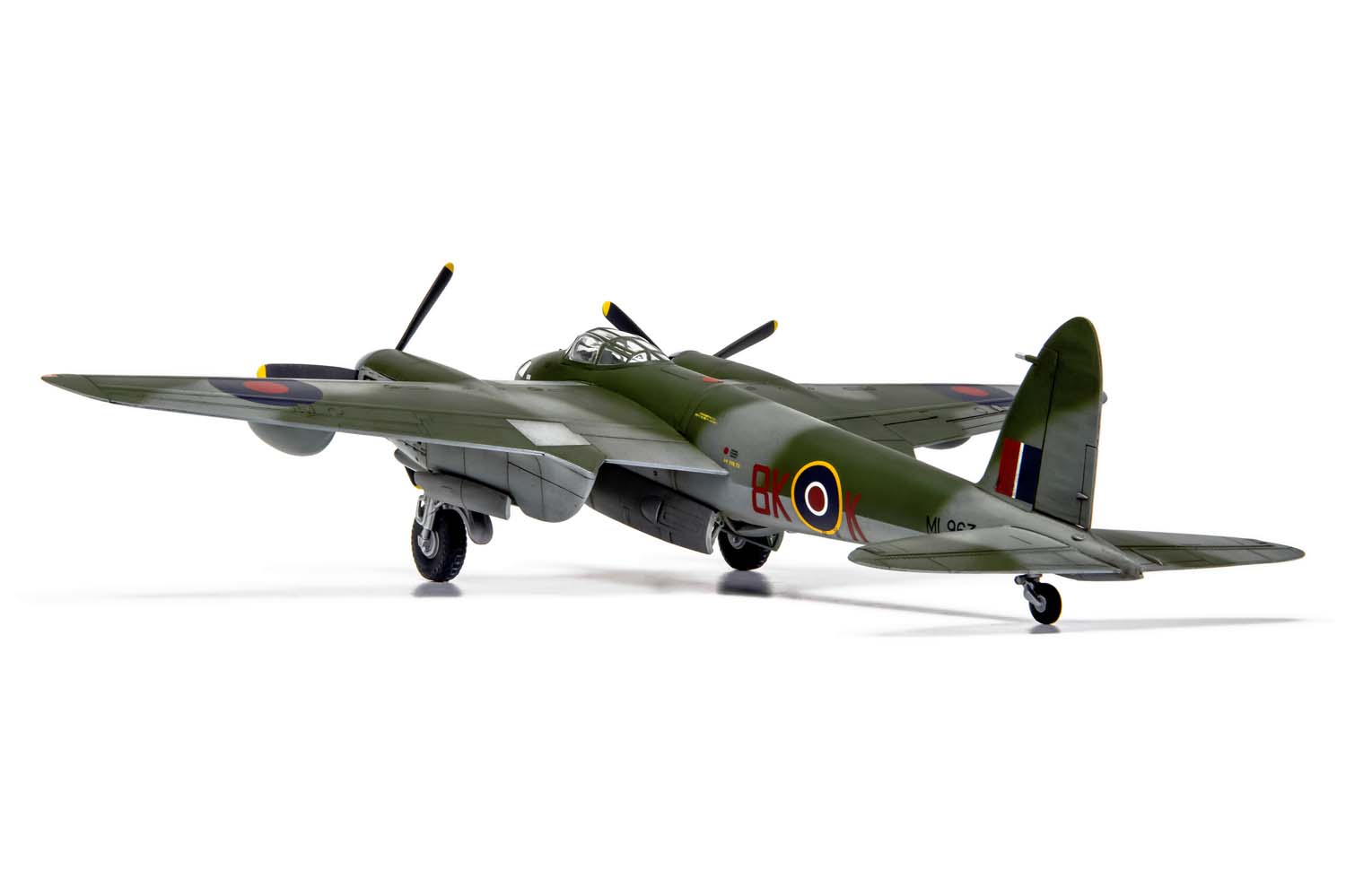
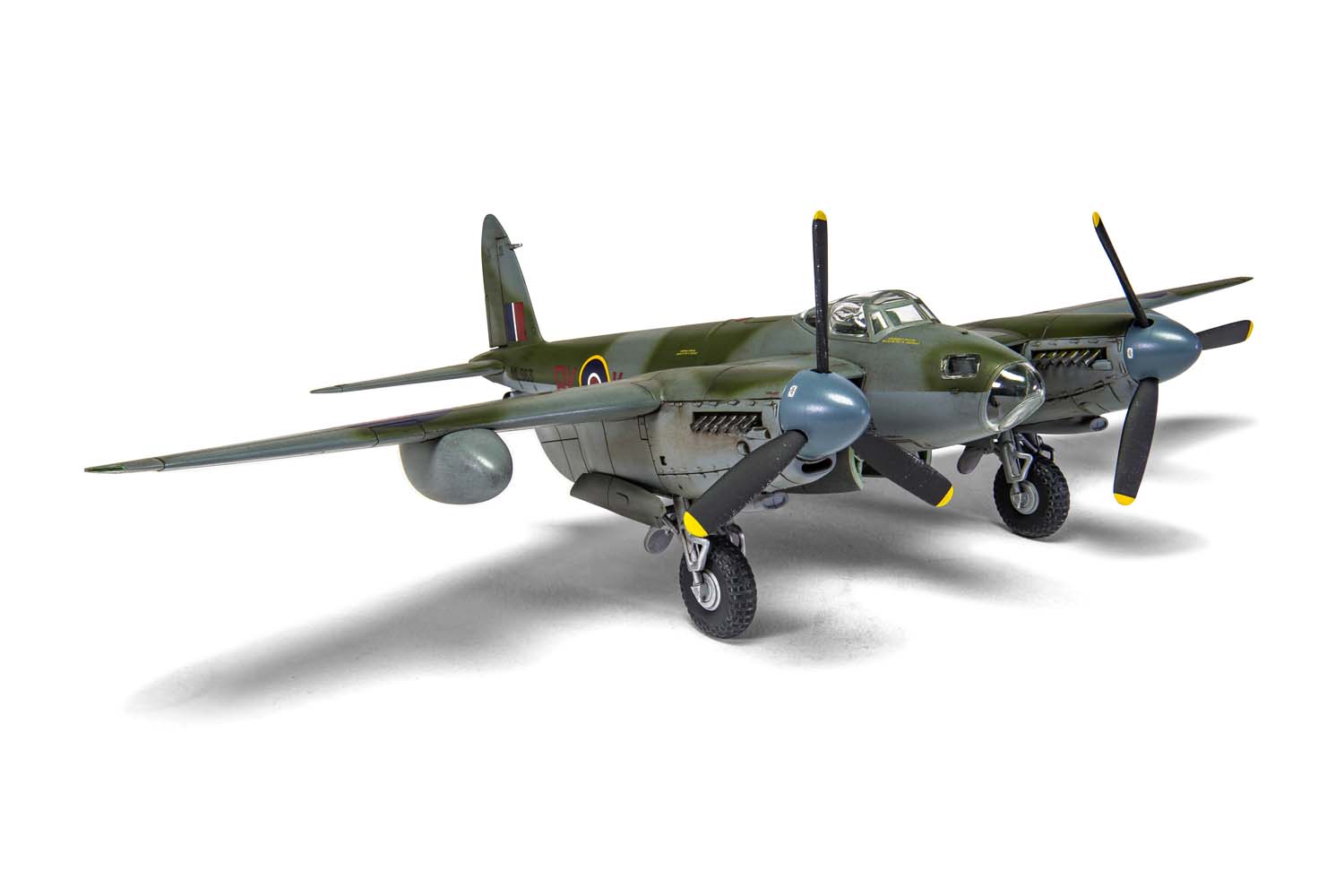
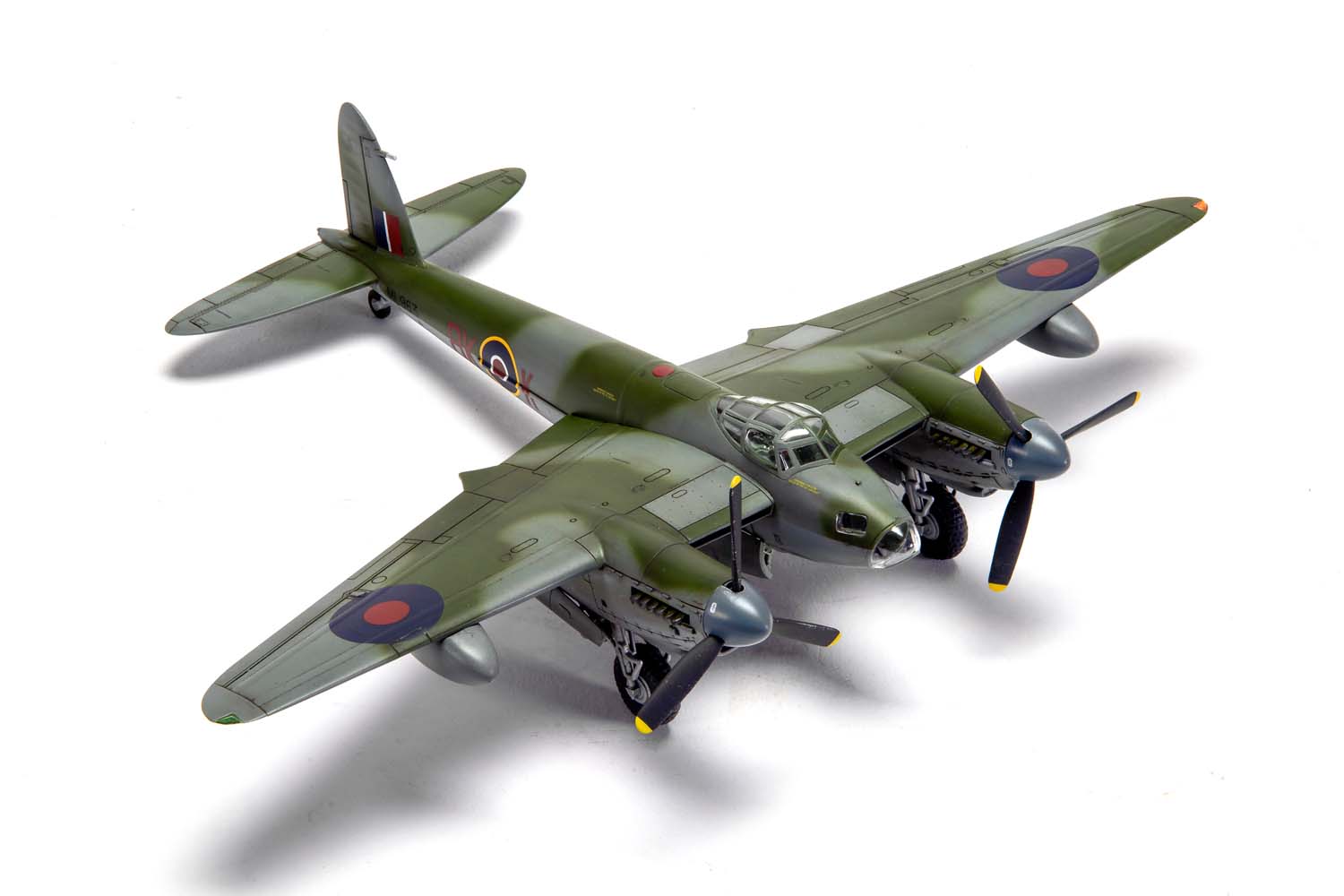
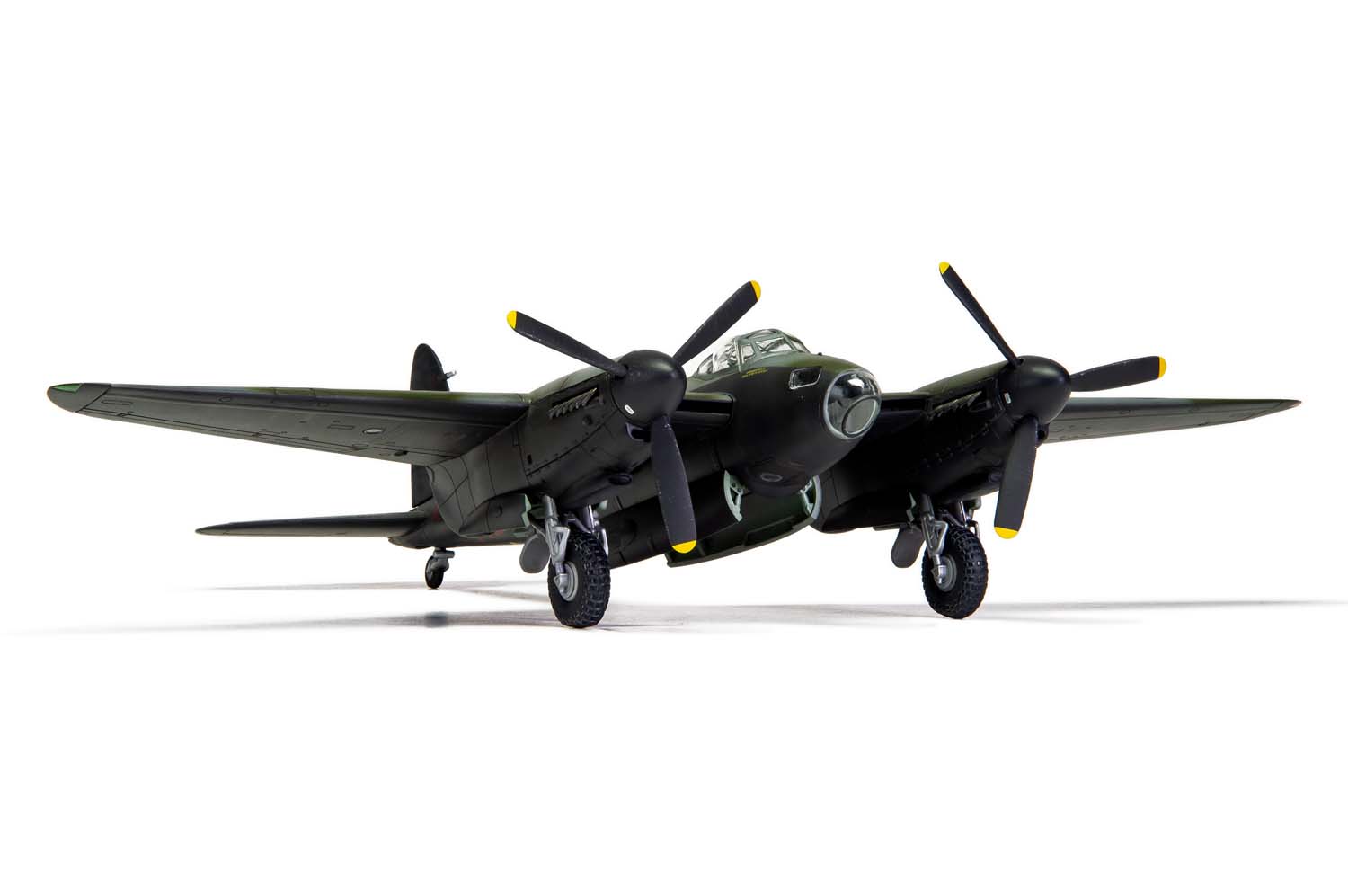
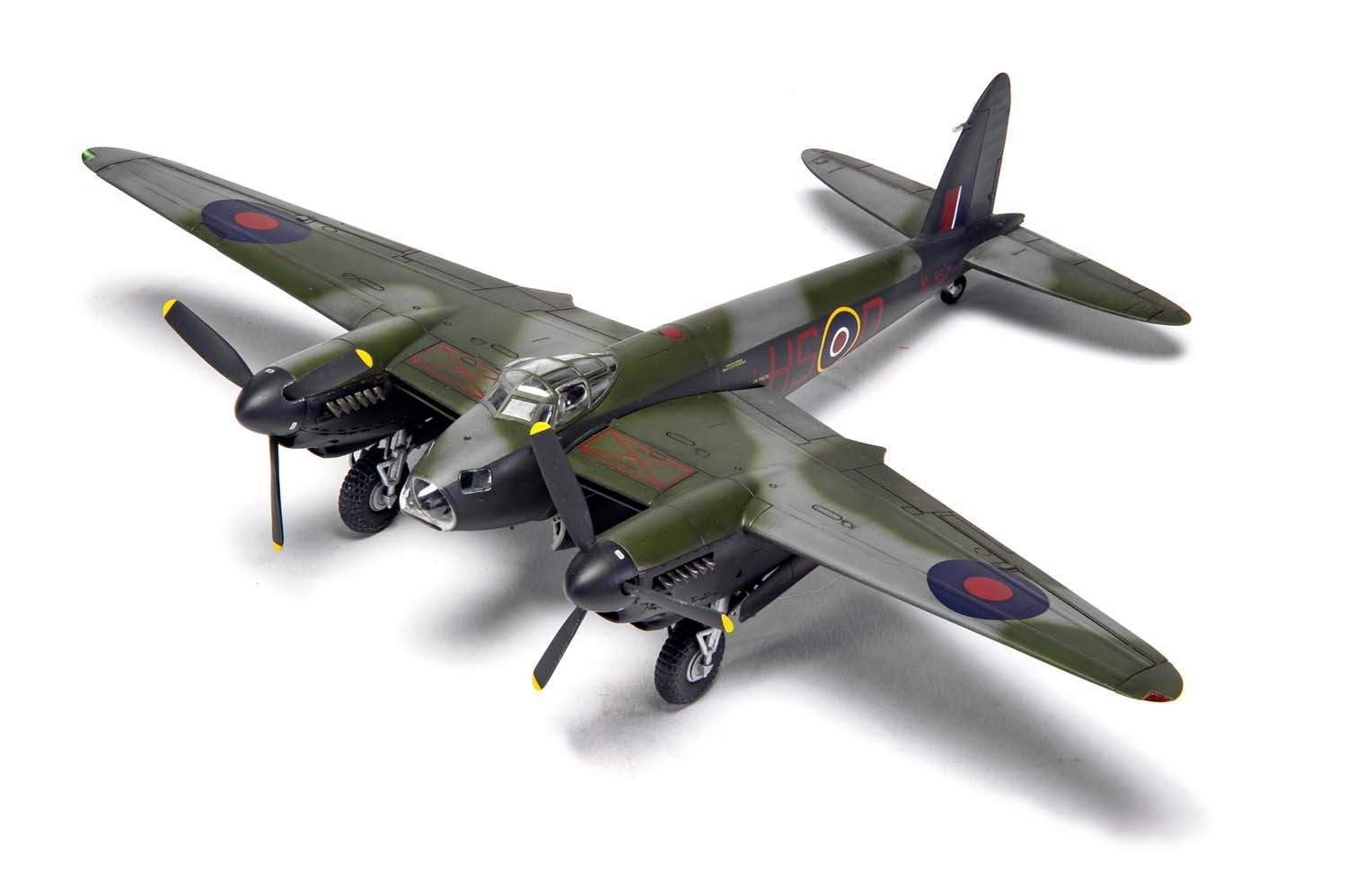
Without question, the de Havilland Mosquito qualifies as one of the finest fighting aeroplanes of the Second World War and one which could claim to be the envy of every other air force, particularly the Luftwaffe, who tried, but never quite managed to produce an equivalent aircraft. A true multi-role aircraft, the Mosquito’s famous nickname ‘The Wooden Wonder’ referenced the fact that this hugely successful British aircraft was constructed using ‘non-strategic’ materials and employed a clever system of balsa and birch plywood lamination, which gave the aircraft great strength. Although they relied on the performance and survivability of their Mosquitos, men in these units would often take its nickname a stage further and affectionately refer to their aircraft as ‘Flying Furniture’.
Developed and tested largely as a private venture and without interference from the Air Ministry, once they saw what de Havilland had managed to produce, the Ministry were suitably impressed and immediately placed an order for 150 aircraft, with the Mosquito quickly attracting a ‘priority status’ production requirement. The Mosquito was one of the fastest aircraft in the world at that time and one which would prove to be something of an aviation phenomenon – although initially intended as a high speed bomber, Mosquitos would also operate as day and night fighters, pathfinders, night intruders, maritime strike and reconnaissance aircraft.
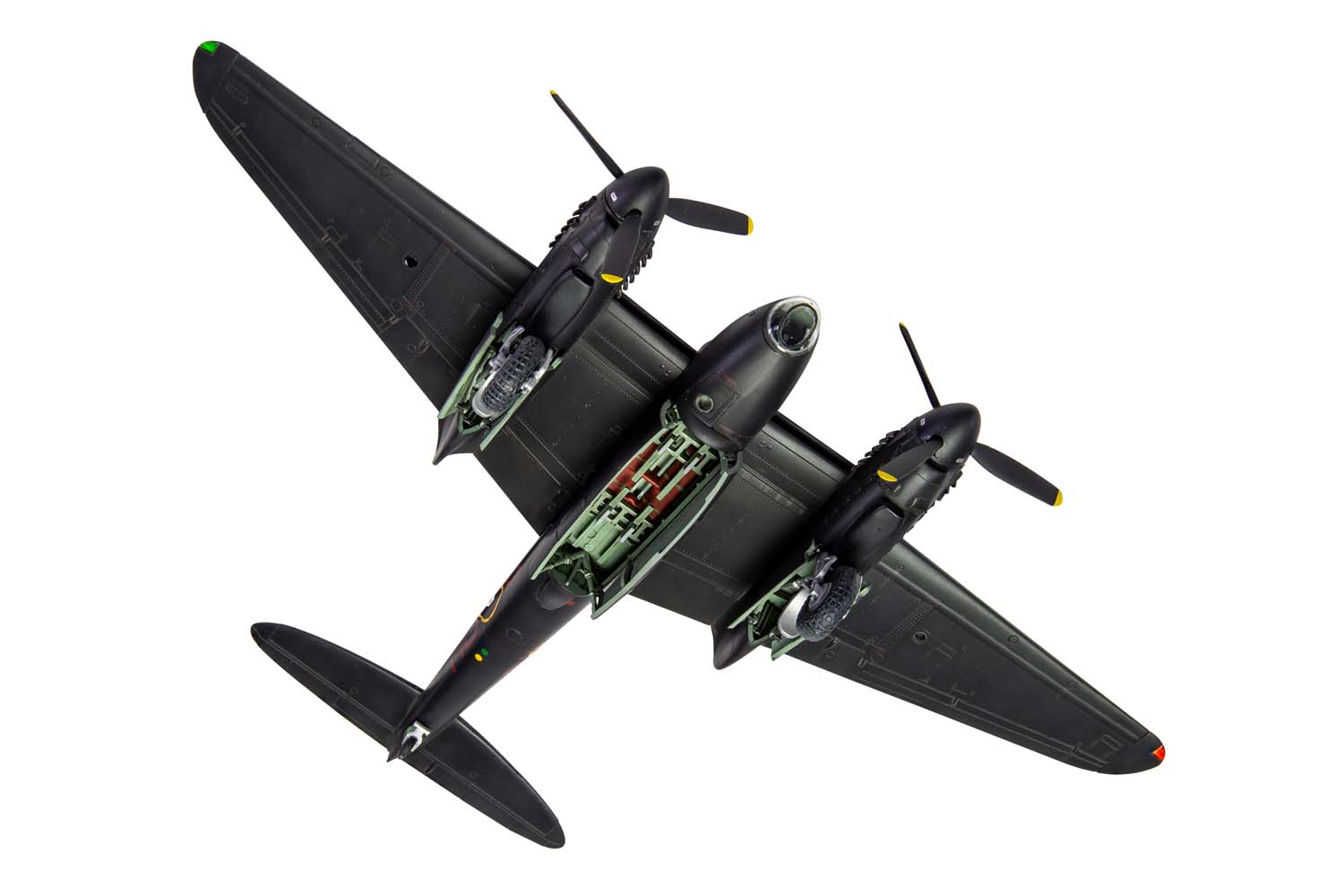
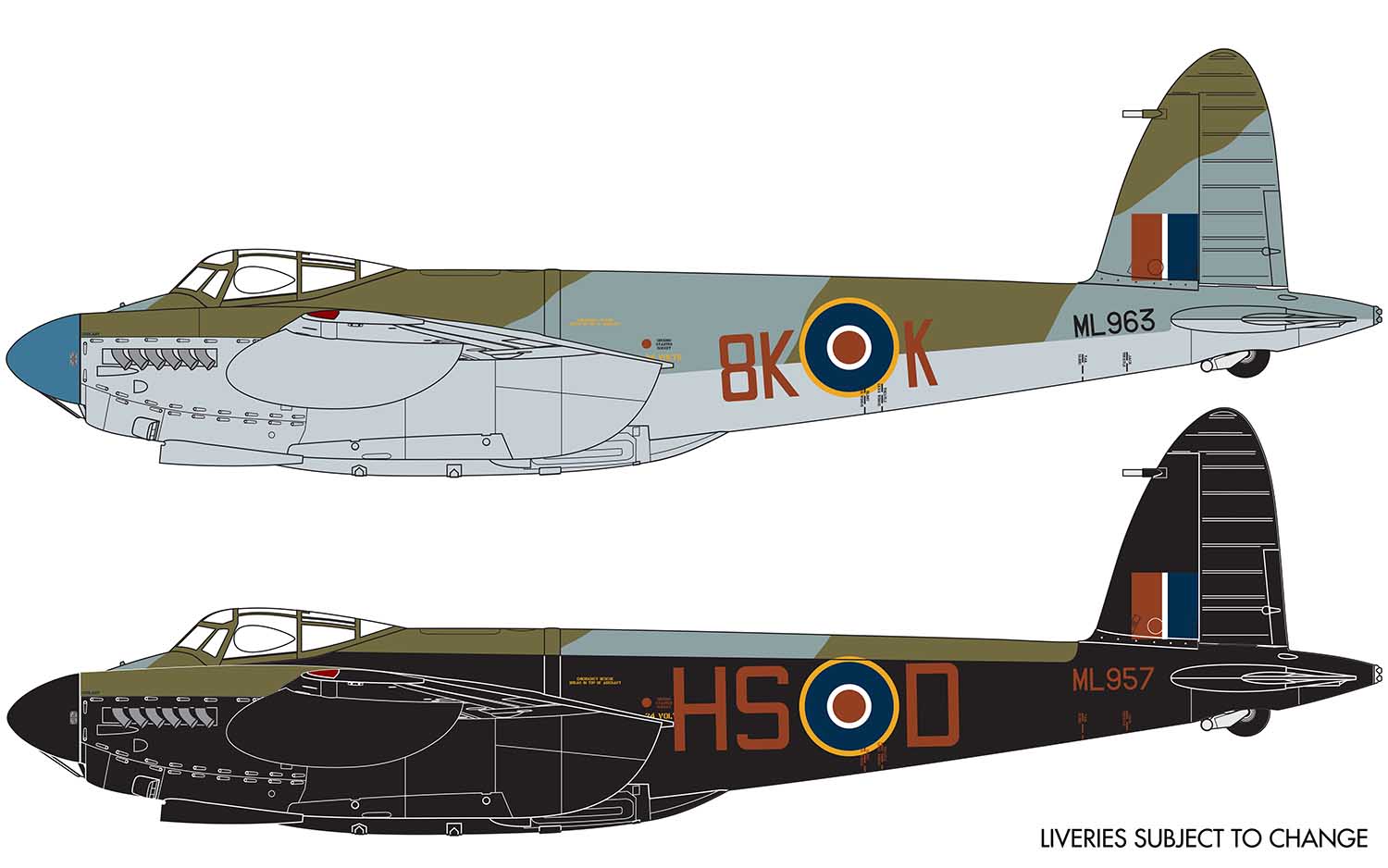
Once the first production aircraft started reaching RAF squadrons towards the end of 1941, the de Havilland Mosquito quickly showed itself to be one of the most valuable assets available to the Royal Air Force, a real war winner and one which would serve with distinction for the remainder of the conflict. Originally conceived as a high speed bomber for the RAF, the final major bomber variant of the de Havilland Mosquito was the B.XVI, with deliveries to front line squadrons starting from 1944. This was a development of the earlier B.IX variant and one which had been optimised for high altitude operation, incorporating a new pressurised cabin. Another unarmed version of the Mosquito, the B.XVI could carry a 3,000lb bomb load, however, all but the first 12 aircraft from a total production run of 402 machines incorporated modifications to allow a 4,000lb ‘Cookie’ or blockbuster bomb to be carried internally, a weapon which possessed devastating destructive capability.
Combining the power of these fearsome weapons with the legendary speed and bombing accuracy associated with Mosquito operations allowed Bomber Command to keep the pressure on the enemy throughout the latter stages of WWII. Interestingly, these huge bombs were exactly four times the weight of the original bomb load this exceptional aircraft was designed to carry, which is testament to the strength of the Mosquito’s construction techniques. Optimised for high altitude operations, this final major bomber variant of the Mosquito could be powered by several different ‘seventy series’ versions of the Rolls Royce Merlin engine, in addition to incorporating a modified wing, which could now accept either a 50 or 100 gallon paper drop-tank on either side and up to four externally mounted 500lb bombs, further enhancing the strategic capabilities of this superb aircraft.
By the end of its ten year production run, which began in 1940, almost 8,000 of these highly effective warplanes had been constructed. For an aircraft which earned such an impressive wartime reputation, it is sobering to think that the Mosquito may have been stopped in its tracks, as Air Ministry officials were initially concerned that work on this new aircraft project might disrupt production of the Tiger Moth training biplane, something they could not allow to happen. Thankfully, designers at de Havilland knew they were on to a winner and were determined to see their magnificent new aircraft fly.